Key Takeaways
- Transformative Impact: Virtual reality (VR) is revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing medical training, patient treatment, and rehabilitation with immersive experiences.
- Applications in Training: VR is utilized for surgical simulations, anatomy education, and scenario-based learning, resulting in improved skill acquisition and retention among healthcare professionals.
- Enhancing Patient Treatment: It plays a significant role in pain management, phobia treatment, and cognitive behavioral therapy, helping to reduce discomfort and anxiety during medical procedures.
- Benefits of Rehabilitation: VR gamifies rehabilitation, motivating patients and providing real-time feedback to improve recovery outcomes and engagement in physical therapy.
- Challenges to Implementation: Adoption barriers include high costs and skepticism among professionals, which can limit access to VR technology in some healthcare settings.
- Future Prospects: The integration of AI, enhanced surgical training, and more affordable VR solutions are set to increase accessibility and effectiveness in healthcare, promoting better patient outcomes.
Virtual reality is transforming healthcare in remarkable ways. This cutting-edge technology is no longer confined to gaming; it’s making significant strides in medical training, patient treatment, and rehabilitation. By immersing users in lifelike simulations, virtual reality provides a unique platform for medical professionals to hone their skills and for patients to confront their fears.
As healthcare continues to evolve, the integration of virtual reality offers innovative solutions to age-old challenges. From pain management to surgical simulations, this technology not only enhances learning but also improves patient outcomes. As the industry embraces these advancements, the potential for virtual reality in healthcare is just beginning to be realized.
Virtual Reality In Healthcare
Virtual reality (VR) revolutionizes healthcare by offering immersive, interactive experiences that enhance various medical processes. Hospitals, clinics, and medical schools utilize VR for training, treatment, and rehabilitation, enabling a deeper understanding of complex medical concepts.
Applications in Medical Training
- Surgical Simulations: Surgeons practice procedures in realistic environments, honing their skills without patient risk.
- Anatomy Education: Medical students explore 3D models of the human body, gaining comprehensive insights that textbook images cannot provide.
- Scenario-Based Learning: Trainees engage in lifelike situations, developing decision-making skills for emergency responses.
Patient Treatment Enhancement
- Pain Management: VR provides distraction techniques for patients undergoing painful procedures, reducing their perception of discomfort.
- Phobia Treatment: Exposure therapy in virtual environments allows patients to confront fears safely and progressively.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Patients engage in guided sessions that promote behavioral changes through immersive interactions.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
- Motivation in Exercise: VR gamifies rehabilitation processes, encouraging patients to participate actively in their recovery.
- Improved Range of Motion: Interactive VR scenarios help patients regain mobility through enjoyable, guided movements.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Real-time performance data collection allows therapists to adjust treatment plans based on individual progress.
- Cost of Implementation: High initial investments in VR technology pose a barrier to widespread adoption in some facilities.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Handling sensitive patient information requires stringent security measures to maintain confidentiality.
- Continued Research: Ongoing studies will explore VR’s potential, establishing evidence-based guidelines for its application in diverse healthcare settings.
Applications Of Virtual Reality In Healthcare
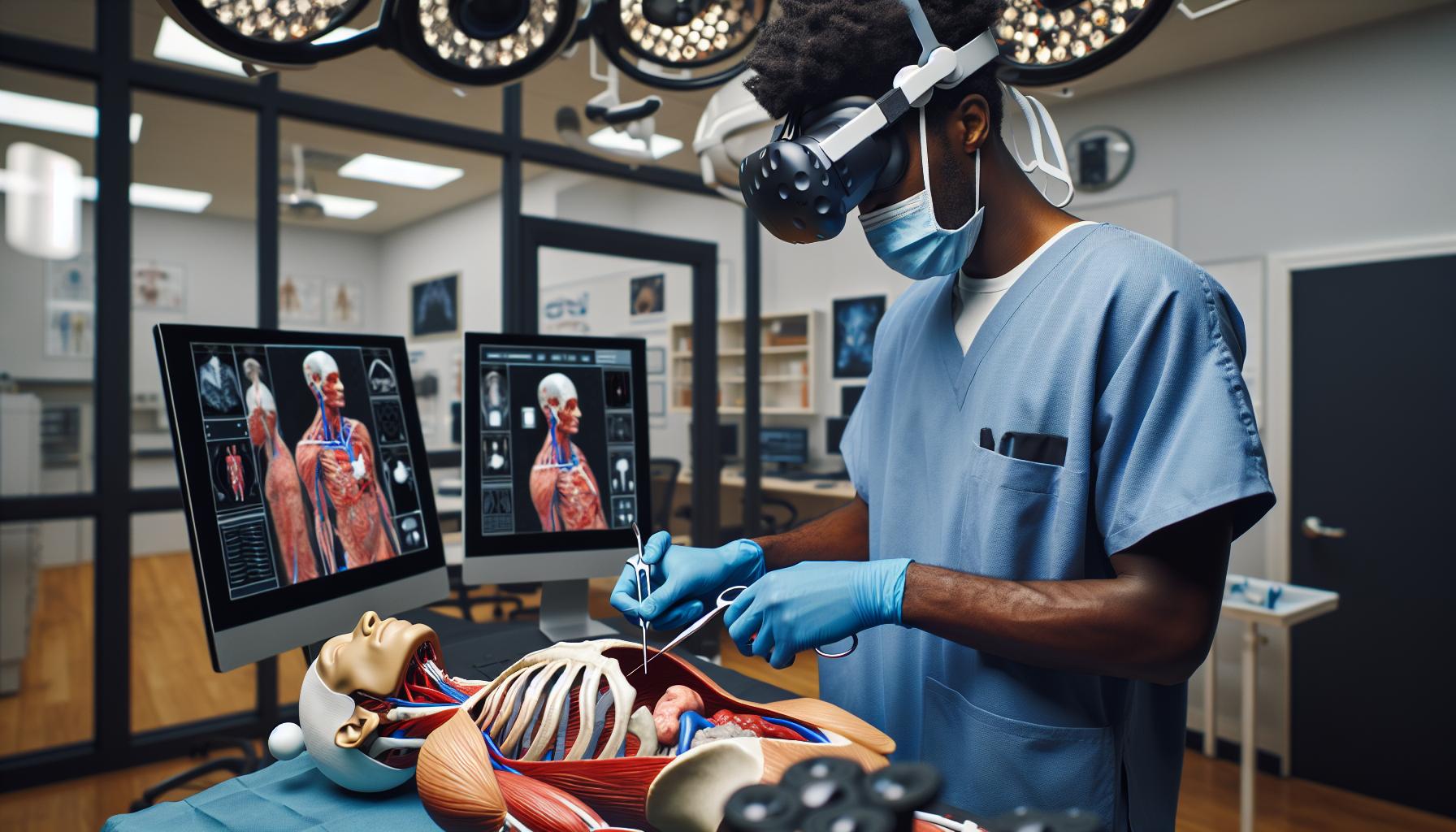
Virtual reality (VR) is revolutionizing healthcare with specific applications that enhance training, rehabilitation, and pain management. These applications demonstrate how VR technology effectively addresses various healthcare challenges.
Surgical Training
Surgical training benefits significantly from VR through immersive simulations. Trainees practice procedures in lifelike environments without risk to patients. They can manipulate 3D anatomical models, enhancing their understanding of complex surgeries. Studies show that VR training improves surgical skills retention and performance in real-world scenarios, with some research indicating a 230% increase in skill acquisition compared to traditional methods.
Patient Rehabilitation
Patient rehabilitation utilizes VR to motivate and engage individuals in their recovery process. VR systems gamify exercises, making them more enjoyable and encouraging adherence to rehabilitation programs. Patients experience real-time feedback during movements, allowing therapists to adjust treatment plans effectively. A study published in the Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation found that patients using VR showed a 30% greater improvement in motor function compared to those receiving standard physiotherapy.
Pain Management
VR plays a vital role in pain management by providing distraction during painful procedures or chronic pain conditions. By immersing patients in virtual environments, their attention shifts away from discomfort, leading to reduced pain perception. Research indicates that patients using VR during treatments report a 24% decrease in pain levels, enhancing overall comfort. Additionally, healthcare providers implement VR in behavioral therapies to address aspects of pain management through relaxation techniques.
Benefits Of Virtual Reality In Healthcare

Virtual reality (VR) offers numerous advantages in the healthcare sector, significantly enhancing training and patient treatment experiences. Its immersive capabilities lead to improved outcomes for both healthcare professionals and patients.
Enhanced Learning Experience
Enhanced learning occurs through virtual reality’s interactive simulations, which foster deep understanding of complex medical principles. Medical trainees engage in realistic surgical simulations that replicate high-pressure scenarios, allowing them to practice techniques repetitively. Studies demonstrate that trainees using VR exhibit a 230% increase in skill acquisition compared to conventional training methods. Furthermore, anatomy education benefits from 3D visualizations that aid retention of intricate details. Scenario-based learning allows students to manage emergency situations practically, preparing them for real-life applications in clinical settings.
Reduced Patient Anxiety
Reduced patient anxiety is another crucial advantage of virtual reality in healthcare. By creating calming environments, VR alleviates stress during procedures for patients with phobias or anxiety disorders. Studies indicate VR exposure therapy can lead to significant reductions in anxiety levels, with patients reporting a 24% improvement in emotional responses during treatment. Additionally, VR distractions during painful medical procedures help lower perceived pain intensity, making it a valuable tool in pain management. This innovative approach enhances overall patient well-being, promoting positive experiences in healthcare environments.
Challenges And Limitations Of Virtual Reality In Healthcare

Virtual reality (VR) in healthcare presents various challenges and limitations that can hinder its effective implementation and widespread adoption. Key issues include costs and the technology’s integration into existing systems.
Cost Of Implementation
High costs associated with VR technology significantly impact adoption rates in healthcare settings. Expenses encompass hardware, software, and necessary training for staff. A comprehensive VR setup, including headsets and specialized equipment, may exceed $100,000, presenting a financial barrier for smaller facilities. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and upgrades add to long-term costs. Budget constraints can restrict access to advanced training tools for healthcare providers, ultimately affecting the quality of patient care.
Technology Adoption
Technology adoption rates vary across healthcare institutions, influencing the integration of VR solutions. Skepticism among healthcare professionals regarding the efficacy of VR technologies hinders acceptance. Traditional training methods remain deeply entrenched in many medical programs, limiting willingness to embrace new approaches. Furthermore, the learning curve associated with VR systems requires time and resources that many facilities may not afford. Without sufficient investment in training and education, healthcare providers struggle to implement VR effectively, thereby stalling innovation in patient care.
Future Trends In Virtual Reality In Healthcare
Virtual reality (VR) technology is poised for substantial advancement in healthcare. Innovations will lead to enhanced therapeutic applications, further integrating VR in treatment protocols. Key trends shaping the future include:
- Telehealth Integration
VR will merge with telehealth services, allowing remote consultations and patient monitoring. This integration ensures continuous care and accessibility for patients, especially in underserved areas.
- Personalized Therapy
Future VR applications will leverage data analytics and AI to create customized treatment plans. Personalization will enhance therapy effectiveness, particularly in mental health and rehabilitation contexts.
- Enhanced Surgical Training
Advanced VR simulations will replicate rare surgical scenarios, providing medical professionals with diverse training experiences. This training will improve preparedness for complex procedures, ultimately elevating surgical outcomes.
- Pain Management Applications
Future VR programs will expand in pain management settings, incorporating real-time biometric feedback. By adjusting visual stimuli based on patient responses, practitioners can optimize distraction techniques during procedures.
- Greater Accessibility
As technology advances, more affordable VR solutions will emerge. Facilities will adopt these solutions, enhancing access for patients and healthcare providers without substantial financial investments.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration
VR will foster collaboration among specialists by creating immersive environments for joint training and treatment planning. This interdisciplinary approach will refine treatment strategies and improve patient care efficiency.
- Long-term Monitoring and Support
VR systems will evolve to offer ongoing monitoring of patient progress post-treatment. Virtual environments will assist in sustaining engagement in therapy and rehabilitation, promoting better long-term outcomes.
- Research and Development Expansion
Continued investment in R&D will drive innovations in VR therapeutics. Rigorous studies will validate VR’s efficacy, ensuring it becomes a staple in evidence-based healthcare practices.
These trends indicate a transformative shift towards a more integrated, personalized healthcare system, driven by advancements in virtual reality technology.
Landscape Of Healthcare
Virtual reality is reshaping the landscape of healthcare in remarkable ways. Its applications in medical training and patient treatment are not just innovative but essential for improving outcomes. As healthcare professionals continue to embrace this technology, the potential for enhanced learning experiences and effective therapies grows exponentially.
While challenges like cost and skepticism remain, the future of VR in healthcare looks promising. With ongoing advancements and research, VR is set to become a standard tool in medical practice. The integration of VR with telehealth and personalized therapies will likely create a more efficient and patient-centered healthcare system. As this technology evolves, it promises to unlock new possibilities for both practitioners and patients alike.